
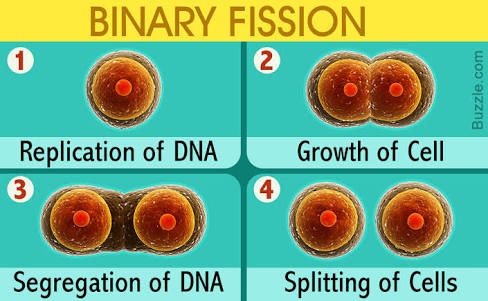
The single DNA molecule first replicates, then attaches each copy to a different part of the cell membrane. Binary fission results in the reproduction of a living prokaryotic cell (or organelle) by dividing the cell into two parts, each with the potential to grow to the size of the original. This form of asexual reproduction and cell division is also used by some organelles within eukaryotic organisms (e.g., mitochondria). Organisms in the domains of Archaea and Bacteria reproduce with binary fission. (1) growth at the centre of the bacterial body. Blue and red lines indicate old and newly generated bacterial cell wall, respectively. The fission may be binary fission, in which a single organism produces two parts, or multiple fission, in which a single entity produces multiple parts.īinary fission Schematic diagram of cellular growth (elongation) and binary fission of bacilli. The object experiencing fission is usually a cell, but the term may also refer to how organisms, bodies, populations, or species split into discrete parts. For the binary fission of atomic nuclei, see Nuclear fission.įission, in biology, is the division of a single entity into two or more parts and the regeneration of those parts to separate entities resembling the original. However, when exposed to harsh conditions like drought, it can slow down its growth rate until more favorable conditions arise."Binary fission" redirects here. Under normal circumstances, it can divide every 48 hours. For instance, the Deinococcus radiodurans is an extremophilic bacteria that can survive a thousand times more radiation than a person can. These bacteria can survive extremely harsh conditions such as high temperatures, high salinity, highly acidic environments, and more. On the other end of the spectrum are the extremophiles. It divides every 15 to 20 hours, which is very slow when compared to other pathogenic bacteria such as Escherichia coli, which can divide every 20 minutes. Mycobacterium tuberculosis is the bacterium that causes tuberculosis in humans. The ambient temperature of the human body is 37 ☌, which means many of the disease-causing bacteria are mesophiles. For instance, mesophiles thrive at moderate temperatures ranging from 20 ☌ to 45 ☌. These conditions include pH levels, temperature, oxygen, light, moisture, osmotic pressure.
The process of binary fission is usually rapid, and its speed varies among species.When the cell starts to get drawn apart, the original (actual) and replicated chromosomes get apart. In this process, the single DNA molecule begins replication and then attaches each copy to various parts of the cell membrane. Binary Fission occurs without any spindle apparatus formation in the cell.

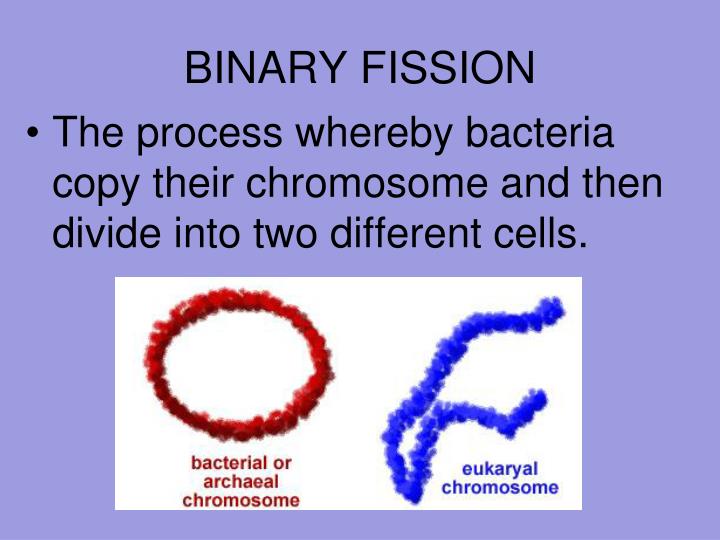
It is a primary method of reproduction in prokaryotic organisms. In this process, each daughter cell receives one copy of its parent DNA.

pumilus, Escherichia coli, Clostridium perfringens, Corynebacterium diphtheriae, Amoeba, Paramecium, Euglena, Ceratium, etc. Organisms that reproduce by binary fission include Bacillus subtilis, B.In protozoans like amoeba, Paramecium, Euglena, however, the process might differ in cell splitting and in how the cytoplasm divides.The process involves the division by utilizing the FtsZ protein, including chromosomal replication, chromosomal segregation, and cell splitting. Most of the bacteria reproduce by this process.Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes are divided by binary fission.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
